Swedish Waste-to-Energy Plants: Pioneering Sustainable Energy
You know, it’s pretty wild how some countries are figuring out what to do with all the stuff we throw away. Sweden, for example, has really got this waste-to-energy thing down. They’re not just burning trash; they’re turning it into power for their cities and heating homes. It makes you wonder why more places aren’t doing the same. They even import trash from other countries because they have so much capacity. It’s a whole system designed to get the most out of what we’d otherwise just bury.
Key Takeaways
- Sweden has built a lot of facilities that turn trash into energy, which is a big part of how they handle waste.
- They recycle a huge amount of their own trash, so very little actually goes into landfills. This means they often need to bring in waste from other countries.
- These plants don’t just make electricity; they also provide heat for entire towns and cities through district heating systems.
- The technology used in places like Sweden Municipal Incinerator facilities is designed to recover as much energy as possible from burning waste.
- By using waste for energy and recycling, Sweden is cutting down on landfill use and working towards a system where materials are reused more.
Sweden’s Advanced Waste-To-Energy Infrastructure
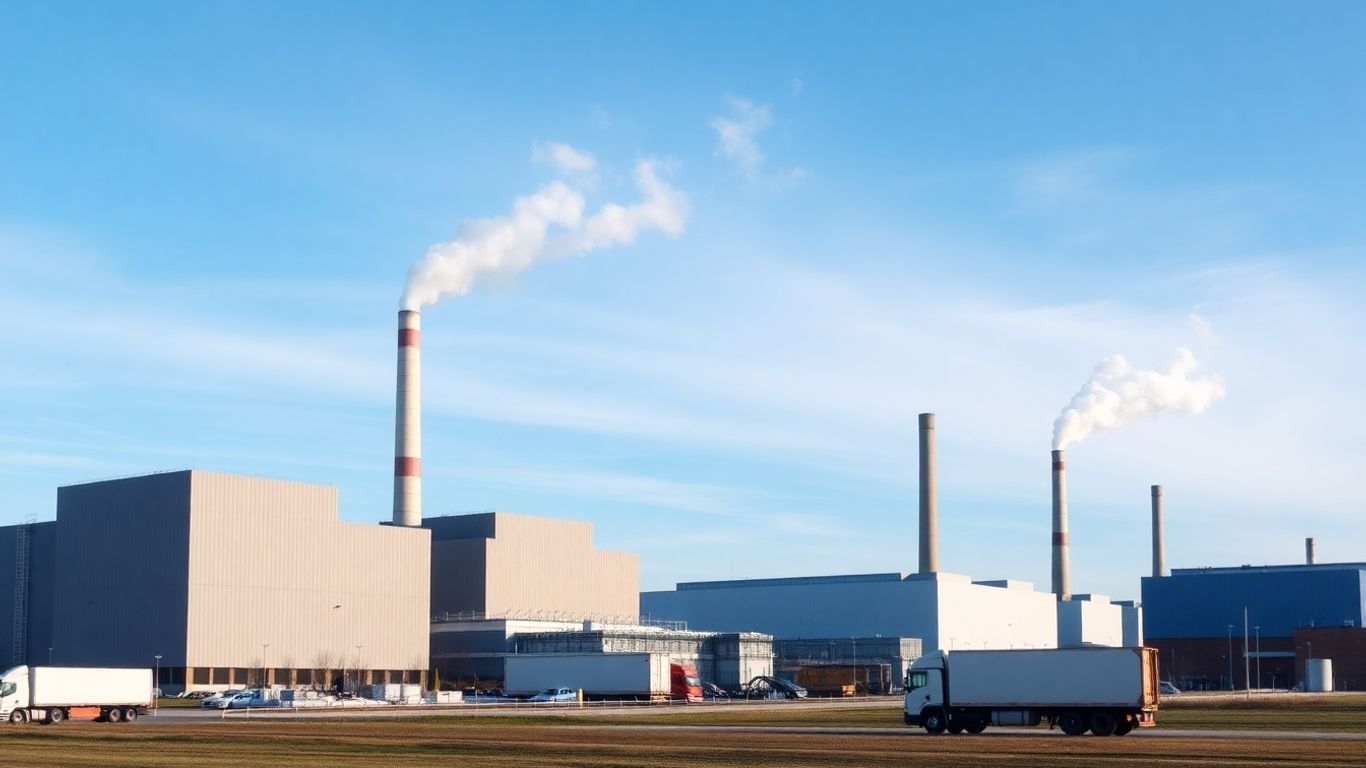

Sweden has really figured out how to handle its trash. It’s not just about throwing things away anymore; it’s about making something useful out of it. They’ve built a whole system that’s pretty impressive, turning what we’d normally consider garbage into power for homes and businesses. It’s a smart approach that tackles waste and energy needs at the same time.
The Role of Waste-To-Energy Plants
These facilities, often called WTE plants, are the heart of Sweden’s system. They take in a lot of the waste that would otherwise end up in landfills. Instead of just sitting there and potentially causing problems, this waste gets processed. The main idea is to burn the waste in a controlled way, and the heat generated from this process is then used to create energy. It’s a pretty neat trick, really.
High Recycling Rates and Landfill Avoidance
What’s really striking is how little waste actually goes to landfills in Sweden. They’ve managed to recycle a huge amount of materials, and the rest is often sent to these WTE plants. This means that the amount of waste piling up in landfills is incredibly small, which is great for the environment. It shows a real commitment to not just managing waste, but reducing its overall impact.
Here’s a look at how waste is handled:
- Recycling
- Waste-to-Energy Plants
- Minimal Landfill
Importing Waste to Sustain Operations
It might sound a bit strange, but Sweden actually imports waste from other countries. Why? Because their WTE plants are so efficient and their own waste production is so well-managed that they sometimes need more material to keep the plants running at optimal levels. This means they’re not only solving their own waste problems but also helping neighbors deal with theirs, all while generating renewable energy.
Sweden’s approach shows that waste doesn’t have to be a burden. It can be a resource, contributing to a cleaner environment and a more sustainable energy supply. This model is something many other countries could learn from.
Transforming Waste into Power
Sweden’s approach to waste management is pretty neat because they’ve figured out how to turn what we throw away into something useful. It’s not just about getting rid of trash; it’s about making power. This is a big part of the whole energy from waste plants Europe scene, and Sweden is definitely a front-runner.
Generating Electricity from Waste Gases
So, how does this actually work? When waste is burned in these special facilities, it releases gases. Instead of letting those gases just go into the air, Sweden captures them. These gases are then used to spin turbines, which in turn generate electricity. It’s a clever way to get power without relying solely on traditional sources. This process is a key aspect of municipal waste to energy trends globally, showing a shift towards more resourceful waste handling.
- Combustion of waste produces heat.
- Heat boils water, creating steam.
- Steam drives turbines to generate electricity.
This method significantly reduces the volume of waste that would otherwise end up in landfills, turning a problem into a power source.
Providing District Heating for Cities
But it’s not just about electricity. A lot of the heat generated from burning waste is also put to good use. Sweden has a well-developed district heating system, and the waste-to-energy plants feed directly into it. This means that the heat from incinerated trash can warm up homes and buildings across entire cities. It’s a pretty efficient system, especially during the colder months. For example, the Spittelau plant in Vienna, while not in Sweden, shows how these facilities can heat tens of thousands of homes Vienna’s Spittelau incineration plant.
Here’s a quick look at how it contributes:
| Use of Waste Heat |
|---|
| District Heating |
| Industrial Processes |
| Hot Water Supply |
This dual approach – generating both electricity and heat – makes Sweden’s waste-to-energy system incredibly effective. They’re really making the most out of every bit of waste they process.
Leading the Global Waste Management
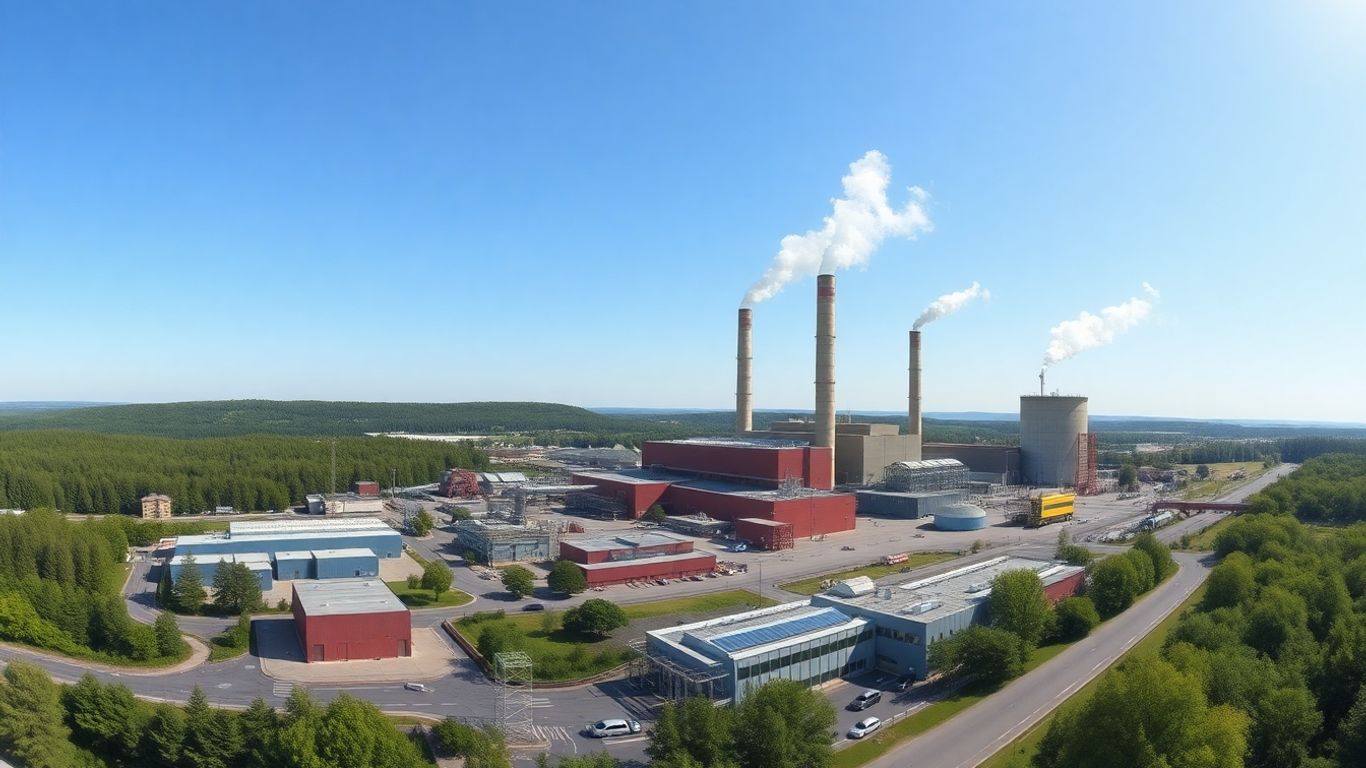

Sweden’s approach to waste management is something other countries are really looking at. They’ve figured out how to turn trash into a resource, which is pretty neat when you think about it. It’s not just about getting rid of garbage; it’s about making power and heat from it.
Sweden’s Commitment to Sustainability
This whole waste-to-energy thing is a big part of Sweden’s plan to be more sustainable. They don’t want stuff just sitting in landfills, polluting the ground. Instead, they’ve built a system that captures the energy from waste. It’s a smart way to handle what we throw away.
- They aim to recycle and recover energy from almost all household waste.
- Landfills are practically a thing of the past in Sweden for household trash.
- This system helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional landfilling.
Sweden’s dedication to this method shows a forward-thinking mindset. They’re not just dealing with today’s waste but also thinking about the future of energy and the environment. It’s a model that many are trying to follow.
Comparison with Other Leading Nations
When you look at how Sweden handles waste, it stands out. Countries like Denmark and Singapore are also doing well in this area, using similar waste-to-energy technologies. But Sweden has been at it for a while and has a really well-established network.
Here’s a quick look at how some countries are doing:
| Country | Percentage of Waste to Landfill (Approx.) | Waste-to-Energy Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Sweden | < 1% | High, imports waste |
| Denmark | Low | High, innovative plants |
| Singapore | Low | Advanced WTE facilities |
It’s clear that these nations are prioritizing turning waste into a useful resource, moving away from the old landfill model. Sweden, in particular, has become a leader because of its extensive infrastructure and its willingness to import waste to keep its energy recovery plants running efficiently. This shows a strong commitment to circular economy principles.
The Mechanics of Sweden Municipal Incinerator Facilities
So, how exactly does Sweden turn trash into power? It’s not magic, though it might seem like it. These municipal incinerator facilities, often called Waste-to-Energy (WTE) plants, are pretty sophisticated operations. They’re designed to handle massive amounts of waste and get as much usable energy out of it as possible, all while keeping environmental impact low. It’s a multi-step process, really.
How Sweden Municipal Incinerators Operate
First off, the waste arrives at the plant. It’s not just dumped anywhere, though. It’s usually stored in a large, enclosed bunker. This helps control odors and dust. Then, a big crane, operated by skilled workers, grabs the waste and feeds it into the furnace. The key is that the waste is burned at very high temperatures. This controlled burning is what generates heat. The air pulled into the furnace is also carefully managed to make sure the combustion is as complete as possible. It’s a bit like a really, really big, high-tech fireplace, but instead of burning logs, it’s burning everything from food scraps to packaging.
The Technology Behind Energy Recovery
Once the waste is burning, the real work begins. The intense heat from the furnace boils water in a boiler, creating steam. Think of it like a giant kettle. This steam is then channeled through a turbine, which is basically a big fan with blades. As the steam pushes the turbine, it spins very fast.
This spinning motion is connected to a generator, and that’s what produces electricity. It’s pretty neat when you think about it – all that stuff we throw away is spinning a machine to power our homes. The steam can also be used directly for district heating systems, warming up buildings and water in nearby cities. It’s a clever way to get a second use out of the heat generated.
Here’s a simplified look at the process:
- Waste Reception: Trash is brought in and stored in a bunker.
- Combustion: Waste is burned at high temperatures in a furnace.
- Steam Generation: The heat boils water, creating high-pressure steam.
- Turbine Operation: Steam spins a turbine.
- Electricity Production: The spinning turbine drives a generator to create electricity.
- Heat Distribution: Excess steam can be used for district heating.
The entire system is designed to be as efficient as possible. Modern plants have advanced filters and scrubbers to clean the gases produced during combustion before they are released into the atmosphere. This is a big deal for reducing pollution. They’re constantly monitoring emissions to make sure they meet strict environmental standards. It’s not just about burning trash; it’s about doing it cleanly and responsibly.
Environmental Benefits of Swedish Waste Management
It’s pretty neat how Sweden has figured out how to turn trash into something useful. Instead of just piling it all up, they’re really good at getting rid of it in ways that help the environment. This approach significantly reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, which is a huge win.
Reducing Landfill Burden
Landfills are a big problem, right? They take up space and can pollute the ground and water. Sweden’s waste management facilities are designed to handle a massive amount of waste, meaning less goes to these traditional dumps. They process so much that they actually import waste from other countries to keep their systems running efficiently. This means fewer landfills are needed overall, both in Sweden and in the countries that send their waste there. It’s a smart way to deal with a growing global issue.
Contributing to a Circular Economy
Sweden is really pushing for a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled as much as possible. Their waste-to-energy plants play a big part in this. Instead of just burning trash, they recover energy from it. This energy can then be used to heat homes or generate electricity. It’s a system that closes the loop, turning what would be waste into a resource. This whole process helps conserve natural resources and reduces the need to extract new materials.
Here’s a quick look at how much waste is managed:
| Waste Stream | Percentage Processed | Percentage Landfilled |
|---|---|---|
| Household Waste | ~99% | <1% |
| Imported Waste | Varies | Minimal |
The focus isn’t just on getting rid of waste, but on extracting value from it. This mindset shift is what makes their system so effective and environmentally sound. It’s about seeing waste not as an endpoint, but as a potential beginning for something new.
These Swedish waste management facilities are a great example of how innovation can tackle environmental challenges. They’ve managed to create a system that not only cleans up waste but also powers communities. It’s a testament to their commitment to sustainability and a model that many other nations could look to for inspiration. You can find out more about advanced incinerator technology here.
The Scale of Sweden’s Waste Processing
When you think about how Sweden processes garbage, it’s pretty impressive. They’ve really figured out how to handle a massive amount of waste, not just from their own country but from others too. It’s not just about burning trash; it’s a whole system designed to get the most out of what we throw away.
Number of Operational Waste-To-Energy Plants
Sweden has a significant number of facilities dedicated to turning waste into usable energy. Currently, there are 32 operational Waste-To-Energy (WTE) plants spread across the country. These plants are the backbone of their waste management strategy, handling a huge volume of materials that would otherwise end up in landfills.
Managing National and Imported Waste Streams
It’s not just Swedish trash that fuels these plants. Because Sweden is so efficient at recycling and recovering energy, they actually import waste from other European countries. This helps keep their WTE plants running at optimal capacity. Think of it like this:
- Domestic Waste: All the garbage generated by Swedish households and businesses.
- Imported Waste: Trash brought in from places like the UK, Italy, Norway, and Ireland.
This dual stream of waste allows Sweden to maximize energy production and further reduce the need for landfills, both at home and abroad. It’s a clever way to manage resources on a larger scale.
Sweden’s approach to waste processing is a testament to their commitment to sustainability. They’ve built an infrastructure that not only deals with waste effectively but also generates valuable energy from it. This system is designed to be efficient and to minimize environmental impact, making it a model for other nations.
It’s fascinating to see how they’ve managed to process nearly all of their waste, with less than 1% actually going to landfills. This efficiency is what allows them to take on waste from other countries, turning a problem into a solution.
So, What’s the Takeaway?
It’s pretty wild to think about, right? That stuff we toss out without a second thought could actually be powering our homes. Sweden’s really showing us all how it’s done, turning almost all their trash into useful energy. They’ve got these special plants that burn waste and make electricity, and they even import garbage from other countries because they have so much capacity. It’s not quite the DeLorean from the movies, but it’s a smart way to deal with waste and get power at the same time. Makes you wonder when the rest of the world will catch up, doesn’t it?
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Sweden turn trash into energy?
Sweden has special plants called Waste-To-Energy (WTE) facilities. These plants burn trash in a controlled way. The heat from burning the trash creates steam, which then spins turbines to make electricity. It’s like using the trash’s energy to power our homes and cities.
Does Sweden have a lot of trash?
Actually, Sweden doesn’t produce enough trash to keep all its energy plants running! That’s why they import trash from other countries, like the UK and Norway. This helps their plants operate efficiently and also helps their neighbors deal with their waste.
What happens to the trash that isn’t burned for energy?
Sweden is really good at recycling. They recycle most of their trash, like plastic, paper, and metal. Only a tiny amount, less than 1%, actually goes to landfills. The rest is either recycled or used to create energy.
Is burning trash bad for the environment?
Swedish plants are designed to be very clean. They have advanced technology to clean the smoke before it goes into the air, so it doesn’t cause much pollution. By using trash for energy, they also avoid filling up landfills, which can harm the environment.
Can trash also provide heat for homes?
Yes! Besides making electricity, the heat from burning trash is also used to warm up water. This hot water is then sent through pipes to heat up homes and buildings in cities, a system called district heating. It’s a smart way to use the trash’s energy twice.
How many of these trash-to-energy plants does Sweden have?
Sweden has around 32 Waste-To-Energy plants spread across the country. These plants are a big part of how Sweden manages its waste and generates power, making them a leader in this field.








One Comment