The Ultimate Guide to Off-Grid Fuel Storage Safety and Efficiency
Thinking about living off the grid? Or maybe you just want a solid backup plan for when the power goes out? Either way, knowing how to handle your Off-Grid Fuel Storage is a big deal. It’s not just about having power; it’s about having it safely and making sure it lasts. This guide will walk you through everything, from picking the right stuff to keeping it all running smoothly and efficiently.
Key Takeaways
- Off-Grid Fuel Storage is super important for reliable power when you’re not hooked up to the main grid.
- Picking the right batteries, like lithium-ion or lead-acid, depends on your needs and budget.
- Always figure out how much power you actually use before buying storage, so you don’t overspend or come up short.
- Installing your Off-Grid Fuel Storage system safely and keeping it maintained is key for it to last a long time.
- There are lots of ways to use Off-Grid Fuel Storage, from powering a remote cabin to keeping your RV going on trips, and you can make it even better by adding solar and monitoring systems.
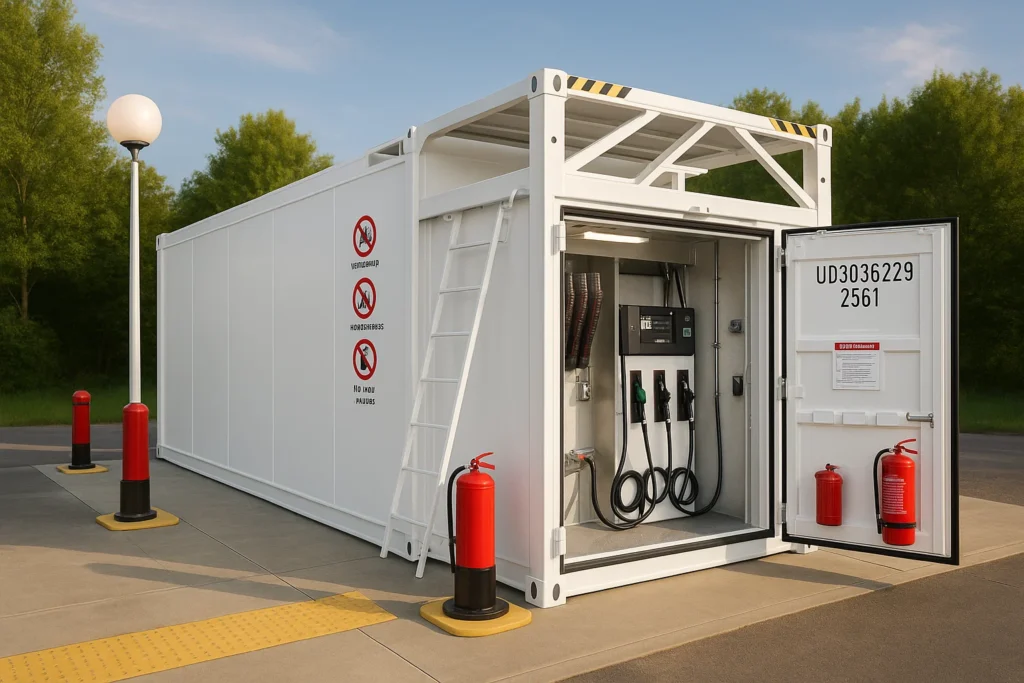

Understanding Off-Grid Fuel Storage Essentials
The Importance of Off-Grid Fuel Storage
Living off the grid means you’re in charge of your own power. That’s why having a solid plan for off Grid Fuel Storage systems is super important. It’s not just about having power when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing; it’s about being truly independent. Think about it: if the main power grid goes down, or if you’re way out in the boonies, your own stored fuel is what keeps the lights on, the fridge cold, and everything else running. It’s about being prepared for anything, whether it’s a short-term outage or a long-term commitment to self-sufficiency. Without reliable storage, your off-grid setup is basically just a fair-weather friend.
Being able to store energy means you can use it whenever you need it, not just when it’s being generated. This flexibility is what makes off-grid living practical and comfortable, giving you peace of mind that you’ll always have power for your daily needs.
Key Components of Off-Grid Fuel Storage Systems
When you’re putting together an off-grid fuel storage system, you’re looking at a few main parts that all work together. It’s not just one big tank; it’s a whole setup. Here are the main things you’ll typically find:
- Storage Containers: These are the actual tanks or containers where you keep your fuel. They come in all sorts of sizes and materials, depending on what kind of fuel you’re storing and how much. For example, you’ll find specific best fuel storage containers for off-grid living, designed to be durable and safe.
- Charge Controllers: If you’re using solar panels or wind turbines to generate electricity, a charge controller is a must-have. It manages the flow of power from your generation source to your batteries, making sure they don’t get overcharged or damaged. This helps keep your batteries healthy for a long time.
- Inverters: Most of your household appliances run on AC (alternating current) power, but batteries store DC (direct current) power. An inverter changes that DC power from your batteries into usable AC power for your home. It’s the bridge between your stored energy and your devices.
- Monitoring Systems: These systems let you keep an eye on your fuel levels, battery charge, and overall system performance. Knowing how much power you have left and how efficiently your system is running is key to managing your off-grid life effectively.
Benefits of Reliable Off-Grid Fuel Storage
Having a dependable off-grid fuel storage setup brings a lot of good things to the table. It’s more than just convenience; it’s about security and freedom. Here are some of the big benefits:
- Energy Independence: This is probably the biggest one. You’re not tied to the utility company anymore. You generate and store your own power, which means you’re in control. This is especially important for energy storage in remote areas or for those who want to be completely self-sufficient.
- Fuel Point: This is the designated system or area for accessing and dispensing fuel from storage containers. A fuel point typically includes pumps, hoses, and safety features to ensure efficient and safe fuel transfer for generators, vehicles, or other equipment.
- Emergency Preparedness: If there’s a natural disaster, a widespread power outage, or any other emergency, you’re ready. Safe off-grid fuel storage for emergency preparedness means you’ll have power for essential services like heating, cooling, and communication when others are left in the dark. This includes having off-grid diesel and gasoline storage solutions for generators or vehicles.
- Cost Savings Over Time: While the initial setup can be an investment, over the long haul, you’ll save money by not paying monthly utility bills. Plus, you’re protected from rising energy costs.
- Environmental Benefits: If you’re storing energy from renewable sources like solar or wind, you’re reducing your carbon footprint. It’s a greener way to live, and you’re contributing to a more sustainable future.
- Flexibility and Mobility: For those with RVs, tiny homes, or mobile setups, reliable fuel storage means you can take your power with you. You’re not limited by where the grid reaches. This also includes knowing how to store fuel in extreme cold climates off the grid, ensuring performance in harsh conditions.
Selecting the Right Off-Grid Fuel Storage Batteries
Choosing the right battery for your off-grid setup is a big deal. It’s not just about picking something that holds a charge; it’s about finding a power source that fits your lifestyle, your energy needs, and your budget. You’ve got a few main options, and each one has its own quirks and benefits. Let’s break them down.
Deep Cycle Lead-Acid Battery Options
Lead-acid batteries have been around forever, and for good reason. They’re reliable, and they’ve been the go-to for off-grid systems for a long time. Think of them as the workhorses of the battery world. They come in a couple of flavors:
- Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA): These are the classic ones. They need a bit of looking after, like checking the water levels every now and then. They’re usually the cheapest upfront, which is nice if you’re on a tight budget.
- Sealed Lead-Acid (SLA) or Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA): These are more hands-off. You don’t have to add water, and they’re generally safer because they don’t vent gases as much. They cost a bit more than FLAs, but the reduced maintenance can be worth it.
While lead-acid batteries are a solid, budget-friendly choice for many off-grid setups, their lifespan and maintenance requirements mean they might not be the best long-term solution for everyone. It’s a trade-off between initial cost and ongoing effort.
Advanced Lithium-Ion Battery Solutions
Lithium-ion batteries are the new kids on the block, and they’re pretty impressive. They’re lighter, smaller, and can hold a lot more power for their size. They also last a lot longer than lead-acid batteries, which is a huge plus. If you’re looking for a modern, efficient power solution, off-grid solar batteries are definitely worth considering. Here’s why:
- High Energy Density: They pack a lot of power into a small space.
- Longer Lifespan: They can handle way more charge and discharge cycles than lead-acid batteries, meaning they’ll last for years and years.
- Minimal Maintenance: Once they’re set up, you pretty much forget about them.
- Faster Charging: They can charge up much quicker than lead-acid batteries.
While the upfront cost of lithium-ion batteries is higher, their extended lifespan and efficiency often make them more cost-effective over the long haul.
Comparing Battery Technologies for Off-Grid Fuel Storage
So, how do you choose? It really comes down to what you need and what you’re willing to spend. Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide:
| Feature | Deep Cycle Lead-Acid | Lithium-Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan (Cycles) | 500-1,500 | 3,000-10,000+ |
| Maintenance | High (FLA), Low (SLA) | Very Low |
| Efficiency | 70-85% | 90-99% |
| Weight/Size | Heavy/Bulky | Lighter/Compact |
| Temperature Range | Narrower | Wider |
Think about your daily energy use, how much space you have, and how much you want to tinker with your system. If you’re looking for a set-it-and-forget-it solution with a long life, lithium-ion is probably your best bet. If you’re on a tight budget and don’t mind a bit of maintenance, lead-acid could work for you. Either way, doing your homework now will save you headaches later.
Critical Considerations for Off-Grid Fuel Storage

Assessing Your Energy Consumption Needs
Before buying batteries, fuel tanks, or bladders, figure out how much power and fuel you use. List all appliances and their wattage, estimate daily usage hours, and calculate daily kilowatt-hour (kWh) needs. Consider surge loads for motors or compressors. A thorough energy audit prevents overspending or power shortages.
It’s not just about what you think you use, but what your appliances and devices actually draw. This means looking at everything from your fridge to your phone charger. Getting a clear picture of your daily and peak energy consumption is the first and most important step in designing an effective off-grid fuel storage system. If you get this wrong, you’ll either spend too much on a system that’s way bigger than you need, or worse, you’ll constantly run out of power. You can do this by:
- Listing all appliances and their wattage.
- Estimating how many hours each appliance runs per day.
- Calculating daily kilowatt-hour (kWh) usage.
- Considering surge loads for motors or compressors.
It’s easy to underestimate your power needs, especially when you’re used to unlimited grid power. Take the time to do a thorough energy audit. This will save you headaches and money down the road.
Environmental Factors and Fuel Storage Performance
Where you put your fuel storage system matters a lot. The environment can really mess with how well your batteries work and how long they last. Things like temperature, humidity, and even how much dust is in the air can impact performance. For example, lead-acid batteries don’t like extreme cold, and lithium-ion batteries can lose efficiency in very hot conditions. You need to think about:
- Temperature Fluctuations: Batteries and fuel tanks perform best within specific ranges. Extreme heat can degrade fuel in tanks, while cold affects battery capacity and fuel viscosity. Fuel bladders are adaptable but need protection from freezing.
- Humidity and Moisture: High humidity can corrode fuel tanks and connections. Fuel bladders are less prone but must stay dry to avoid mold.
- Ventilation: Fuel tanks storing volatile fuels like gasoline release vapors, requiring ventilation. Fuel bladders also need ventilated storage.
- Dust and Debris: Dust can clog battery vents or fuel point equipment. Fuel bladders need clean surfaces to avoid punctures.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Battery Performance |
|---|---|
| High Temperature | Reduced lifespan, decreased efficiency |
| Low Temperature | Reduced capacity, slower charging |
| High Humidity | Corrosion, potential short circuits |
| Poor Ventilation | Gas buildup, overheating |
Budgeting for Off-Grid Fuel Storage Systems
Let’s be real, setting up an off-grid system isn’t cheap. But it’s not just about the initial cost of the batteries and solar panels. You’ve got to think about the long-term expenses too. Sometimes, spending a bit more upfront on higher-quality components can actually save you a ton of money over the life of the system. For instance, while propane generators might have a higher initial cost, their long-term fuel efficiency and reliability can make them a smart choice. You need to factor in:
- Initial Equipment Costs: Batteries, inverters, charge controllers, solar panels, and mounting hardware.
- Installation Costs: Labor if you’re not doing it yourself, and any necessary permits.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular checks, cleaning, and eventual replacement of components.
- Fuel Costs: If you’re using a generator as a backup or primary power source.
- Lifespan and Warranty: How long will the components last, and what kind of warranty do they come with? This impacts your long-term replacement budget.
Safe Installation and Maintenance of Off-Grid Fuel Storage
Alright, so you’ve got your off-grid fuel storage system all picked out, which is great. But honestly, that’s just half the battle. Getting it installed right and then keeping it running smoothly? That’s where the real work comes in. Mess this part up, and you’re not just looking at a system that doesn’t work; you could be looking at some serious safety hazards. Nobody wants that. It’s all about being careful and smart from the get-go.
Best Practices for Fuel Storage System Installation
Installing an off-grid fuel storage system isn’t something you just wing. There are some pretty important steps you need to follow to make sure everything is safe and works like it should. First off, always make sure you’re following the manufacturer’s instructions to the letter. Seriously, don’t skip any steps. They wrote those instructions for a reason.
You also need to think about where you’re putting this thing. It needs to be on a stable, level surface, away from anything flammable. Good ventilation is a must, especially if you’re dealing with batteries that can off-gas. And don’t forget about securing everything properly so it doesn’t tip over or get damaged. It’s a bit like building with LEGOs, but with much higher stakes.
Here’s a quick checklist for installation:
- Site Preparation: Clear the area, ensure it’s level, and use a concrete pad for heavy fuel tanks. Fuel bladders need a flat, debris-free surface.
- Ventilation: Install ventilation to prevent gas buildup from batteries and fuel tanks.
- Fuel Point Setup: Ensure the fuel point is accessible, equipped with spill-proof dispensing equipment, and away from ignition sources.
- Wiring: Use appropriate gauge wiring and ensure tight, corrosion-free connections.
- Grounding: Ground all components, including fuel tanks, to prevent shocks and static buildup.
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access to fuel tanks, bladders, and fuel point for maintenance.
Essential Safety Measures for Off-Grid Fuel Storage
Safety isn’t just a suggestion when it comes to off-grid fuel storage; it’s absolutely critical. We’re talking about storing energy, and that comes with risks if you’re not careful. Think about fire prevention, electrical hazards, and even chemical exposure. You need to have the right safety gear on hand, like gloves and eye protection, especially when you’re messing with batteries. And speaking of batteries, make sure you’re not overcharging them or letting them get too hot. That’s a recipe for disaster. Having a fire extinguisher nearby that’s rated for electrical fires is also a really smart move. It’s all about being prepared for the unexpected.
When dealing with off-grid fuel storage, understanding and implementing safe practices for fuel reserves is paramount. This isn’t just about protecting your investment; it’s about protecting yourself and your property from potential hazards. A little bit of caution and preparation goes a long way in preventing accidents and ensuring your system operates reliably for years to come.
Here are some key safety measures:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Insulated gloves, safety glasses, and appropriate clothing.
- Fire Extinguishers: Keep a Class C extinguisher nearby.
- Spill Kits: Have absorbent materials for electrolyte or fuel spills from tanks or bladders.
- Warning Signs: Post signs about electrical and flammable hazards.
- Regular Inspections: Check for loose connections, damaged wiring, or corrosion in fuel tanks and fuel points.
Implementing Battery Management Systems for Longevity
So, you’ve got your batteries, and they’re installed safely. Now, how do you make sure they last as long as possible? That’s where a Battery Management System, or BMS, comes in. Think of it as the brain of your battery bank. It monitors everything: voltage, current, temperature, and even the state of charge for each individual cell.
This is super important because it prevents things like overcharging or deep discharging, which can really shorten a battery’s life. A good BMS will also balance the cells, making sure they all work together efficiently. It’s like having a tiny, super-smart mechanic constantly looking after your batteries, making sure they’re always in tip-top shape. Proper generator installation is also key for overall system health.
Benefits of a good BMS:
- Overcharge Protection: Prevents batteries from being charged beyond their safe limit.
- Over-discharge Protection: Stops batteries from being drained too low, which can cause irreversible damage.
- Cell Balancing: Ensures all cells in a battery pack are charged and discharged evenly.
- Temperature Monitoring: Shuts down the system or reduces current if temperatures get too high or too low.
- Fault Detection: Alerts you to any issues or malfunctions within the battery bank.
Real-World Applications of Off-Grid Fuel Storage
Optimizing Off-Grid Fuel Storage for Efficiency

When you’re living off the grid, making every watt count is a big deal. It’s not just about having enough power; it’s about using that power smartly so your system runs smoothly and lasts a long time. Think of it like this: you wouldn’t just pour gas into a leaky tank, right? Same goes for your off-grid energy.
You want to make sure you’re getting the most out of every bit of energy you generate and store. This means looking at how you capture energy, how you convert it for use, and how you protect your batteries from damage. Efficient fuel management for remote homesteads is about maximizing every energy input and output. It’s about creating a system that works for you, not against you, ensuring you have reliable power when you need it most.
Maximizing Solar Energy Capture for Fuel Storage
Getting the most out of your solar panels is the first step in efficient off-grid fuel storage. It’s not just about slapping panels on a roof; it’s about smart placement and maintenance.
- Angle and Orientation: Your panels need to face the sun directly for as much of the day as possible. In the Northern Hemisphere, this usually means facing south. The angle should change with the seasons to match the sun’s path. For example, a steeper angle in winter helps catch lower sun rays.
- Shading Avoidance: Even a small shadow on one part of a panel can drastically reduce the output of the entire array. Trim trees, avoid placing panels near chimneys, and be mindful of any structures that might cast a shadow during different times of the day or year.
- Regular Cleaning: Dust, dirt, pollen, and even bird droppings can build up on panels, blocking sunlight. A simple wipe-down with water and a soft brush can make a big difference in energy capture. Think of it as giving your panels a spa day.
- MPPT Charge Controllers: These devices are super important. They optimize the voltage and current from your solar panels to match what your batteries need, pulling out every last bit of power. It’s like having a smart assistant making sure no energy goes to waste.
Efficient Power Inversion for Off-Grid Fuel Use
Once you’ve captured and stored your energy, you need to convert it into usable AC power for your appliances. This is where your inverter comes in. Not all inverters are created equal, and choosing the right one can significantly impact your system’s efficiency.
- Pure Sine Wave Inverters: These are generally the best choice for off-grid systems. They produce a clean, stable power output that’s just like what you get from the utility grid. This is important for sensitive electronics, motors, and anything with a clock. Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper but can cause issues with some appliances, leading to inefficiency and potential damage.
- Right Sizing: Don’t just guess. You need an inverter that can handle your peak power demands. If your inverter is too small, it will trip or fail when you try to run too many things at once. If it’s too big, it might consume more power just by being on, even when nothing is running. Calculate your total wattage for all appliances you might run simultaneously, then add a buffer.
- Efficiency Ratings: Look for inverters with high efficiency ratings, often 90% or more. This means less energy is lost as heat during the conversion process. Every percentage point matters when you’re relying on stored power.
It’s easy to overlook the small details when setting up an off-grid system, but these seemingly minor choices, like the type of inverter or the angle of your solar panels, add up to significant differences in overall performance and longevity. Paying attention to these aspects from the start can save you headaches and money down the line, ensuring your power supply is robust and reliable.
Preventing Overcharging with Charge Controllers
Charge controllers are the unsung heroes of your off-grid battery system. Their main job is to protect your batteries from overcharging, which can severely shorten their lifespan and even be dangerous. Solar battery storage for homeowners is a key component of any off-grid setup.
- Regulating Voltage and Current: A charge controller monitors the voltage of your batteries and adjusts the current coming from your solar panels. Once the batteries reach a certain voltage (fully charged), the controller reduces or stops the flow of power to prevent overcharging.
- Types of Charge Controllers:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): These are simpler and less expensive. They work by rapidly switching the solar panel connection on and off to maintain the correct charging voltage. They are good for smaller systems or when the solar panel voltage is similar to the battery voltage.
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking): As mentioned before, these are more advanced and efficient. They can convert excess voltage from the solar panels into additional current, meaning they can extract more power from your panels, especially in varying weather conditions. They are highly recommended for larger or more complex systems.
- Battery Health: Preventing overcharging is critical for battery health. Overcharging can lead to electrolyte boiling in lead-acid batteries, or thermal runaway in lithium-ion batteries, both of which are bad news. A good charge controller ensures your batteries are charged safely and efficiently, extending their life and ensuring [efficient fuel management for survival] when you need it most.
Advanced Strategies for Off-Grid Fuel Storage
Integrating Multiple Fuel Sources for Off-Grid Systems
When you’re living off the grid, relying on just one type of fuel can be risky. What if the sun doesn’t shine for days, or the wind stops blowing? That’s why combining different fuel sources is a smart move for true energy independence. Think of it like having a backup for your backup. You might have solar panels as your main power, but then you could also have a small wind turbine or even a generator that runs on propane or diesel.
This way, you’re covered no matter what the weather does or if one system has a hiccup. It’s all about building a resilient system that can handle anything thrown its way. For example, if you’re in an area with long, dark winters, solar alone won’t cut it. Adding a wind turbine or a generator gives you options. This approach also helps with home backup power fuel options during unexpected outages.
Monitoring and Managing Fuel Storage Performance Remotely
Gone are the days when you had to physically check your fuel levels every single day. Now, with modern tech, you can keep an eye on your off-grid fuel storage from pretty much anywhere. This is a game-changer for peace of mind and efficiency. Imagine getting an alert on your phone if your battery bank is running low or if there’s an issue with your charge controller. This kind of remote monitoring lets you react quickly, preventing bigger problems down the line. It’s especially useful for emergency fuel storage solutions in remote cabins or vacation homes where you’re not always present. You can track things like:
- Battery charge status (State of Charge)
- Energy production from solar panels or wind turbines
- Fuel levels in generators or propane tanks
- System alerts for potential issues (e.g., overcharging, low voltage)
Having real-time data at your fingertips means you can make informed decisions about your energy use and ensure your system is always running smoothly. It takes the guesswork out of managing your off-grid power.
Future Trends in Off-Grid Fuel Storage Technology
The world of off-grid energy is always changing, and new tech is popping up all the time. We’re seeing some really cool stuff that’s going to make off-grid living even easier and more efficient. One big area is battery tech. While lithium-ion is great, there’s research into even better, safer, and cheaper options. Also, smart systems that can predict your energy needs and adjust accordingly are becoming more common.
Think about how your phone learns your habits; future off-grid systems will do the same for your energy. This includes better long-term fuel preservation tips and methods for various fuel types. We’re also seeing more focus on solutions for extreme conditions, like best fuel storage methods for freezing temperatures, ensuring reliability no matter the climate. Here are some things to watch out for:
- Solid-state batteries: These promise higher energy density and improved safety.
- AI-powered energy management: Systems that learn your usage patterns and optimize energy flow.
- Hydrogen fuel cells: A clean alternative for long-duration energy storage.
- Modular and scalable systems: Easier to expand your system as your needs grow.
Conclusion
So, there you have it. Getting your off-grid fuel storage right isn’t just about picking a tank and calling it a day. It’s about thinking through everything: what kind of fuel you’re using, where you’re putting it, and how you’re going to keep it safe. You want to make sure you’re doing things smart, not just for your own peace of mind, but for everyone around you too. A little planning goes a long way here, and honestly, it’s worth the effort to get it set up right from the start. Stay safe out there!
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the best battery for off-grid living?
The best battery for off-grid living depends on your specific needs. Lithium-ion batteries are often preferred for their long life and high efficiency. They charge quickly and last longer than other types. However, lead-acid batteries are a more affordable option, though they need more care. Both types are reliable and widely used, so your choice depends on your budget and how much maintenance you’re willing to do.
How much battery power do I need to live off-grid?
To figure out how much battery power you need, first, calculate your daily energy use in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Then, decide how many days you want to have power stored. Multiply your daily energy use by the number of days you want to store power. For example, if you use 10 kWh a day and want three days of backup, you’ll need 30 kWh of battery capacity. It’s always a good idea to add a little extra for bad weather or unexpected high usage.
How long do off-grid batteries typically last?
The lifespan of off-grid batteries can vary. Lithium-ion batteries can last a long time, often 10 to 15 years, if you take good care of them. Lead-acid batteries usually last about 5 to 7 years. How long a battery lasts depends on how often you use it, how well you maintain it, and the weather conditions it’s exposed to. Regular check-ups and proper use can help your batteries last even longer.
Can I mix different types of off-grid batteries?
Yes, you can combine different types of off-grid batteries, but it’s usually not recommended for best performance. Mixing battery types can lead to problems because they have different ways of charging and discharging. This can make some batteries work harder than others, which can shorten their lifespan. It’s best to use batteries of the same type and age for the most efficient and safest system.
How do I maintain my off-grid batteries?
To keep your off-grid batteries working well, make sure they are charged regularly and not completely drained. Keep them in a cool, dry place, away from extreme temperatures. For lead-acid batteries, you might need to check their water levels and clean their terminals. For all batteries, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and maintenance. Using a battery management system (BMS) can also help keep them healthy.
What are the main uses for off-grid batteries?
Off-grid batteries are used in many different ways. They provide power for homes and cabins that are far from the main power grid, ensuring a steady electricity supply. They’re also great for emergency backup systems, keeping essential things running during power outages. Plus, they’re perfect for mobile setups like RVs and boats, giving you power wherever you go without needing to plug into a traditional power source.









5 Comments